
There are two ways in which desiccant dehumidification takes place:
- Passive adsorption: When the regeneration air is not heated before passing through the desiccant wheel, the dehumidification process is called passive adsorption.
- Active adsorption: When sensible heat is added to the regeneration air before it is passed through the desiccant, the dehumidification process is called active adsorption.
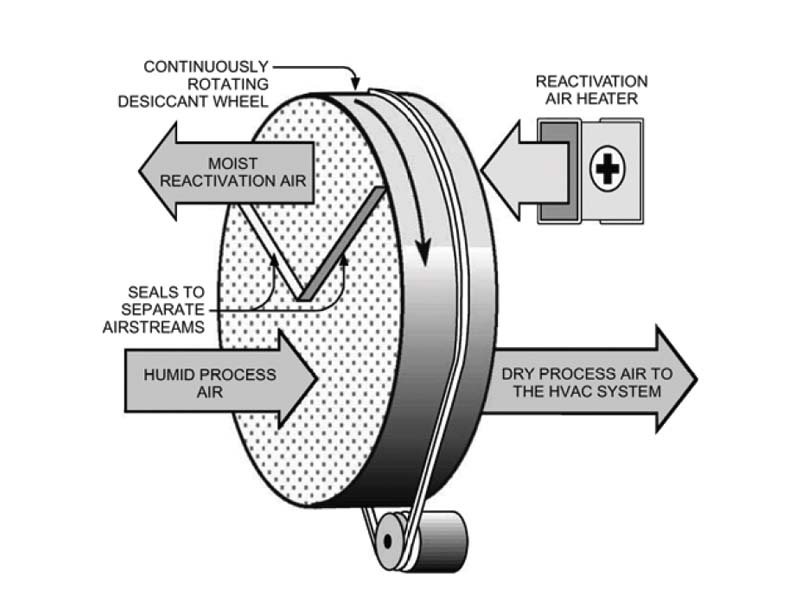
In the first case, the regeneration air undergoes cooling and humidification, whereas in the second case, initially there is heating and then there is cooling and humidification.
Comparison of performances between them
To show how active adsorption helps in removing a greater amount of moisture from process air than passive adsorption in a desiccant dehumidifier, we will perform some calculations as follows:
Using the “Desiccant Wheel Calculator” & “Psychrometric Calculator” by Innovative Air Technologies
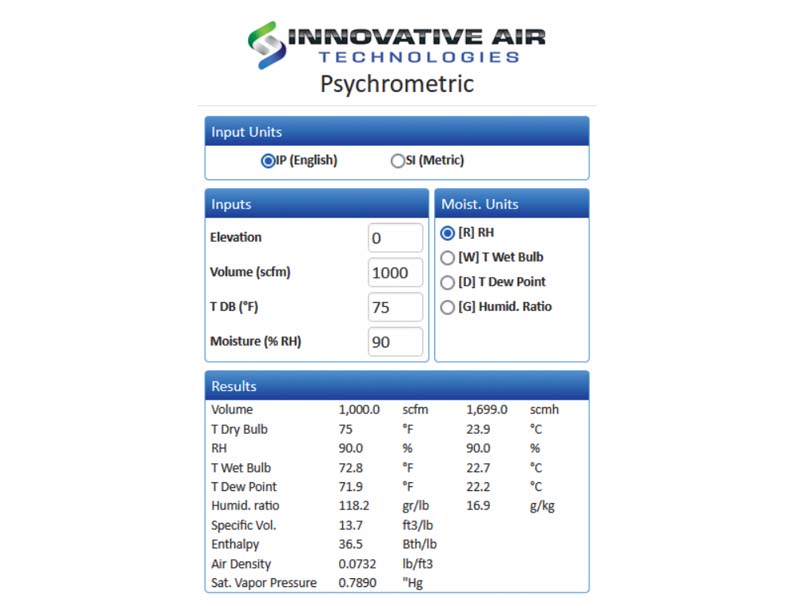
Let the initial condition of process air be 75 °F DB (Dry Bulb), 90% ɸ (Relative Humidity) Þ w (Humidity Ratio) = 118.2 gr./lb. (grains of moisture per pound of dry air) (Psychrometric Calculator)
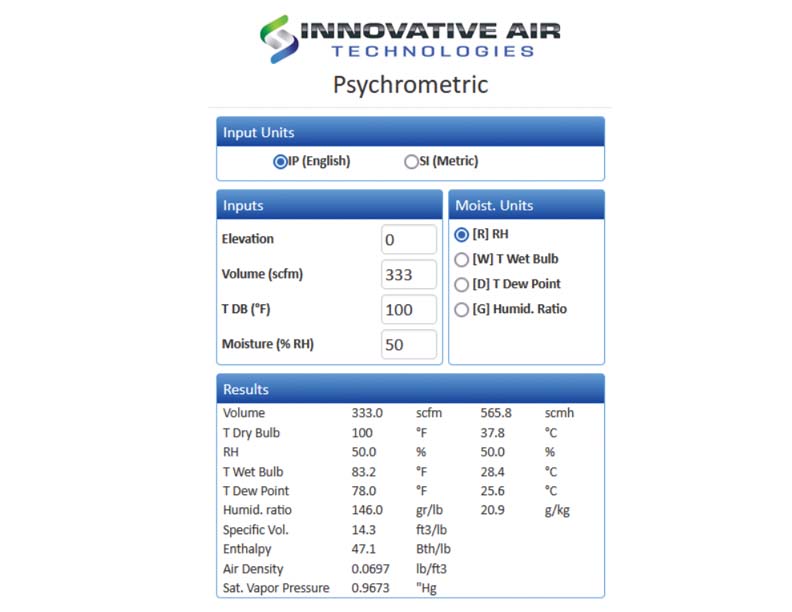
Passive Adsorption: Let the initial condition of regeneration air be 1000F, 50% ɸ Þ w = 146 gr./lb. (Psychrometric Calculator). After inputting the conditions of both the airstreams in the “Desiccant Wheel Calculator”, we find that the humidity ratio of process air has dropped to 111.55 gr./lb.

Active Adsorption: Let’s assume that the regeneration air is preheated to 250 °F using an electric heating coil before passing it through the desiccant wheel. That means only sensible heating has taken place, due to which the moisture content of regeneration air remains same. After inputting the conditions of the 2 airstreams in the “Desiccant Wheel Calculator”, we find that the humidity ratio of process air has dropped to 62.54 gr./lb.
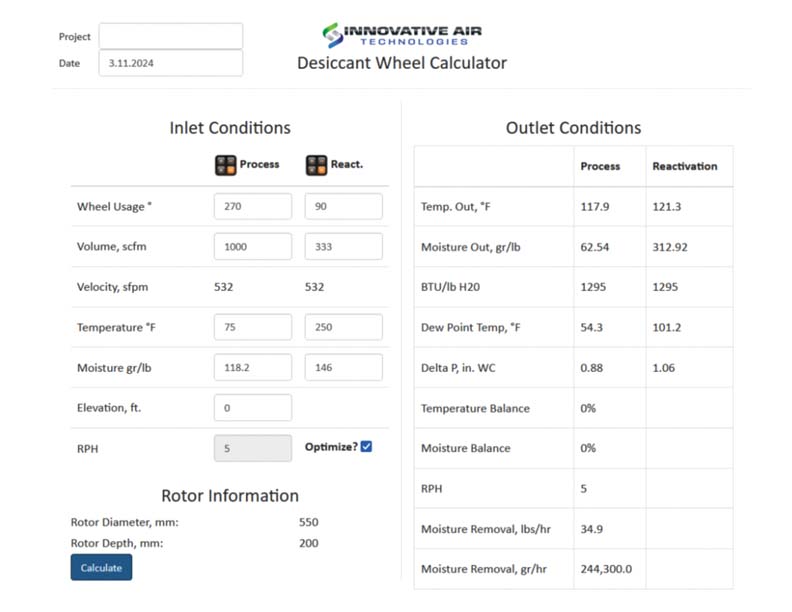
Note: – I’ve made a few assumptions as follows:
- The process air is passing through 270° portion of the wheel, whereas the regeneration air is passing through the remaining 90° portion of the wheel.
2. The volumetric air flow rates of process & regeneration air are 1000 & 333 cfm respectively.
Using the “Daikin Psychrometrics Diagram Viewer” by Daikin Europe NV
By using this tool, let us perform a psychrometric analysis on a psychrometric chart.
Passive adsorption: Let the initial condition of regeneration air (P1) be 100 °F DB, 50% ɸ Þ 83.2 °F WB, 145.5 gr./lb. HR. If this airstream passes through the desiccant wheel, then let’s assume that adiabatic humidification will happen, which is a constant Wet Bulb (WB) process (In practice, the regeneration air does not undergo a perfect adiabatic humidification process, but close to it.) Let’s assume that this airstream is humidified till its maximum capacity.
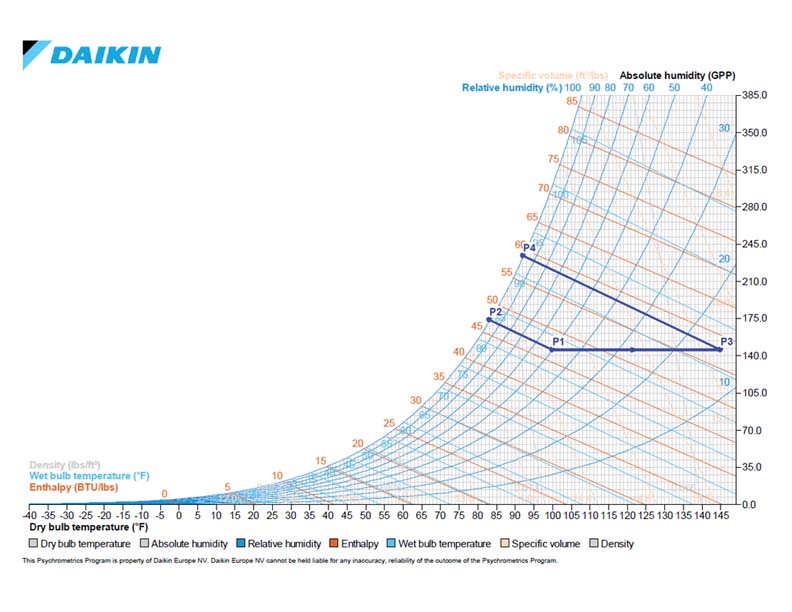
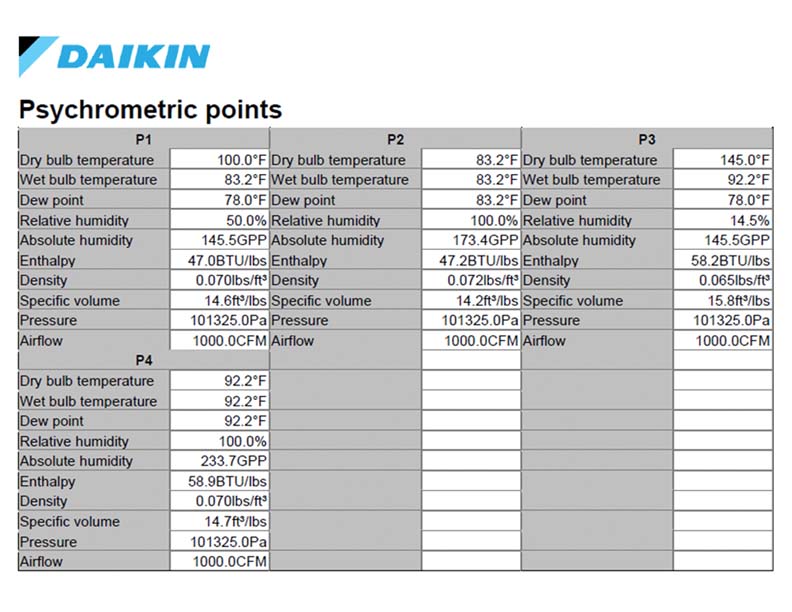
⸫ P2 = 83.2 °F WB, 100% ɸ Þ HR = 173.4 gr./lb. Hence from P1 to P2, the moisture absorption capacity of the airstream was (173.4 – 145.5) = 27.9 gr./lb.
Active adsorption: Let the regeneration air be passed through an electric heating coil (sensible heating) & preheated to 150 °F. That means the ‘w’ at set points P1 & P3 is the same. Let’s assume that this preheated airstream is humidified till its maximum capacity.
⸫ P4 = 92.2 °F WB, 100% ɸ Þ HR = 233.7 gr./lb. Hence from P3 to P4, the moisture absorption capacity of the airstream was (233.7 – 145.5) = 88.2 gr./lb.
Applications:
Passive adsorption is used for total energy wheels to precondition outdoor air. This leads to downsizing of HVAC equipment.
Active adsorption is used for applications requiring exceptionally dry air.
Conclusion
During the operation of rotary desiccant wheels, since active adsorption of regeneration air has more capacity to remove moisture from the process air than passive adsorption, the appropriate type of adsorption process should be selected as per the application.

Rushikesh Jog possesses a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering and a Post-Graduate diploma in HVAC. He is currently working as an HVAC Design Engineer at Proficient, a pharmaceutical consultancy firm. Proficient provides various services such as pharmaceutical facility design, validation, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) compliance, etc…








